Diabetes and pregnancy

Diabetes and pregnancy
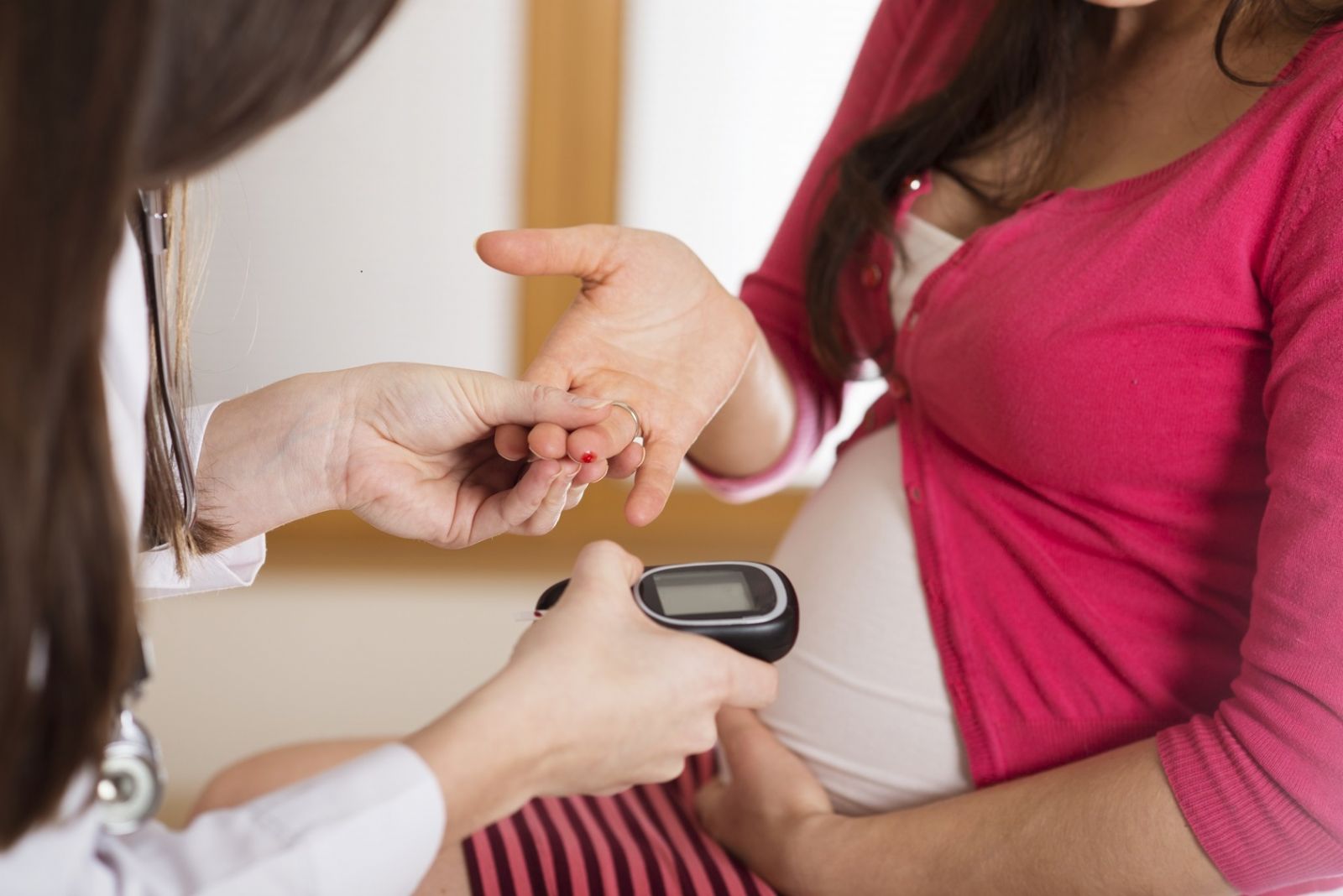
Sometimes women can develop diabetes during pregnancy. This condition arises after 20 weeks of pregnancy and is called hestasional diabetes. After the end of pregnancy, blood sugar levels are fully normalized, but in the next pregnancy, hestasional diabetes may recur, or after a while, the mother may develop diabetes Type 2.
Risk factors in the occurrence of hestional diabetes:
- Presence of Type 2 diabetes in family history (in first degree relatives)
- Prediabetes in the mother
- The presence of arterial hypertension in the mother
- The presence of hestasional diabetes in a previous pregnancy
- Polycystosis syndrome of the ovaries
- Large weight baby history (4.5 kg)
- Previous pregnancies resulting in stillbirth
- Detection of sugar in urine
In this regard, pregnancy that develops against the background of diabetes mellitus, the period after pregnancy is accompanied by a risk for the mother and child.
Dangers for the mother:
- Due to the excessive increase in the child's weight, there is a greater probability of caesarean section surgery at birth
- Miscarriages in pregnancy
- High blood pressure
- Danger of preeclampsia and eclampsia
- Premature birth
In newborns:
- Macrosomy (large weight) and associated traumatization at birth (fracture of the collarbone)
- Long-lasting physiological jaundice
- Respiratory distress syndrome and severe asphyxia
- Brain-circulatory disorders of traumatic origin
- There is a high probability of hyperinsulinemia (excess insulin in the blood) and severe hypoglycemia(low blood sugar) after childbirth.
Healthy eating, increased physical activity,and pre-pregnancy body weight control are important preventive measures to prevent diabetes.
09/11/22